
As food components, lipids are also important because: i) are significant in providing organoleptic characteristics (palatability, flavor, aroma and texture) ii) are vehicle for fat soluble vitamins, pigments or dyes and antioxidants, and iii) may act as emulsifying agents and/or promote the stability of suspensions and emulsions. Furthermore, lipids have crucial participation both, in the prevention and/or in the development of many diseases, especially chronic non-communicable diseases, affecting the lipid requirements in humans. Lipids play a key role in the growth and development of the organism, where the requirements of these molecules (mainly fatty acids) will change depending on the age and physiological state of individuals.
Besides fatty acids, cholesterol is another lipid that has important functions in the body, among which are: i) together with phospholipids is important in the formation of cell membranes ii) constitutes the skeleton for the synthesis of steroid hormones (androgens and estrogens) iii) from its structure is derived the structure of vitamin D, and iv) participates in the synthesis of the bile salts and the composition of bile secretion. įatty acids are, among lipids, of crucial relevance in the structure and physiology of the body because: i) forms an integral part of phospholipids in cell membranes ii) are the primary source of energy (9 kcal /g or 37.62 kjoules/g) iii) in infants, provide more than 50% of the daily energy requirements iv) some fatty acids are of essential character and are required for the synthesis of eicosanoids and docosanoids (of 20 and 22 carbon atoms, respectively), such as leukotrienes, prostaglandins, thromboxanes, prostacyclins, protectins and resolvins), and v) some of them may act as second messengers and regulators of gene expression.

A clear example of this importance is the elevated fatty acid concentration present in nerve tissue, especially very long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Lipids have been instrumental in the evolution of species, having important role in the growth, development and maintenance of tissues. The structural, metabolic and nutritional importance of lipids in the body is supported by numerous investigations in different biological models (cellular, animals and humans).
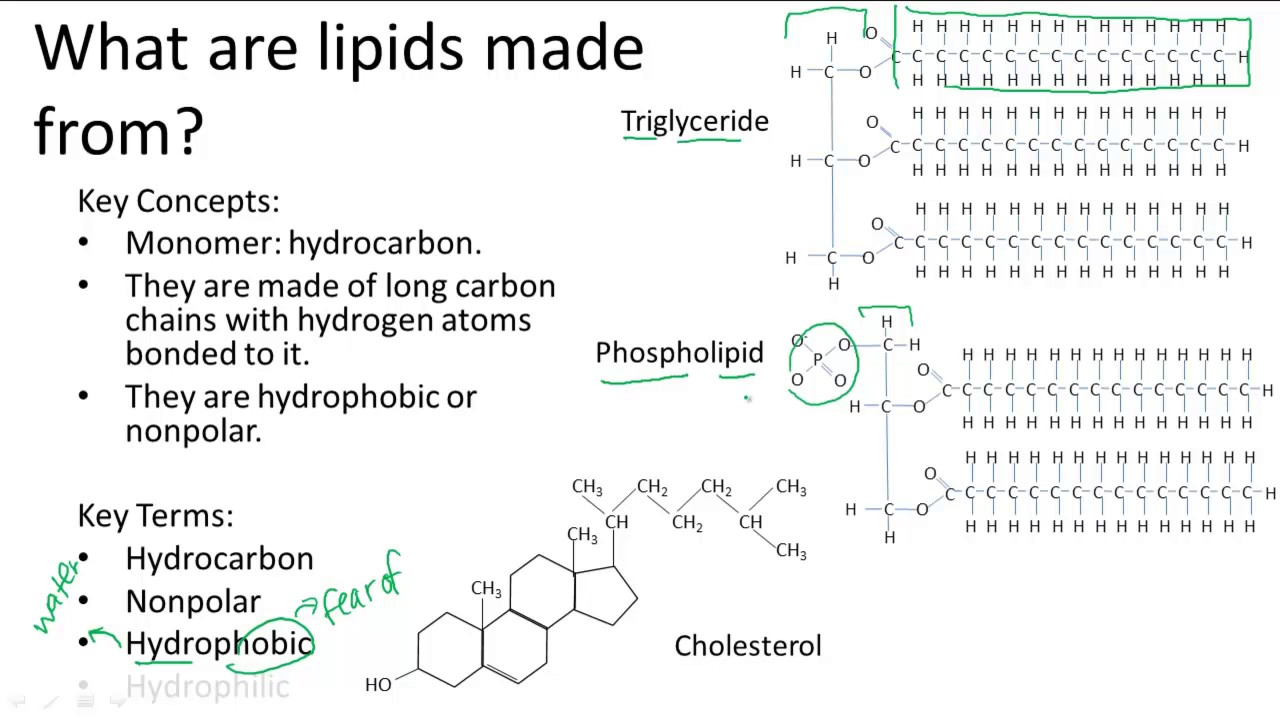
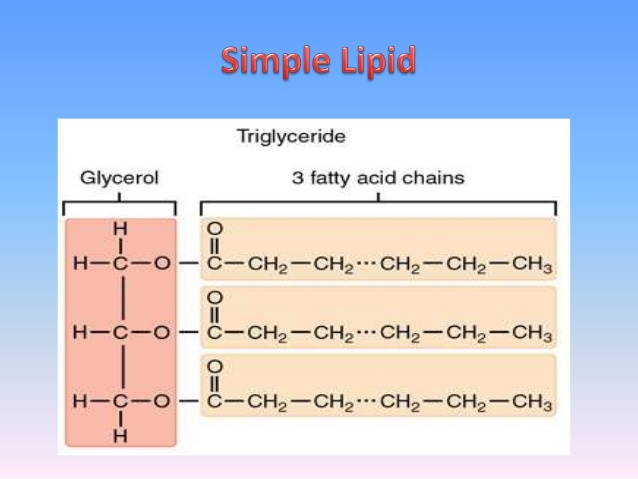
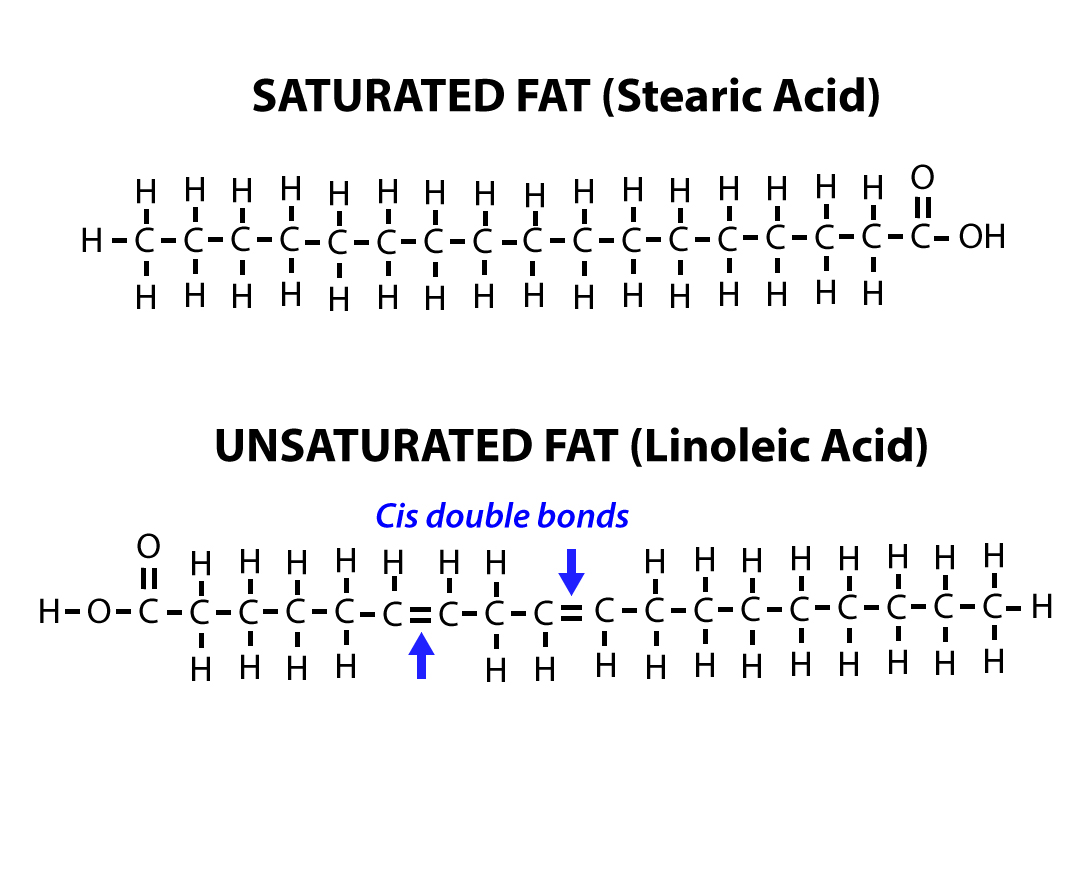
In this context, fats and oils are the main exponents of lipids present in foods and in nutritional processes, being diverse fatty acids and cholesterol the most representative molecules due their important metabolic and nutritional functions. Lipids are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms, and in some cases contain phosphorus, nitrogen, sulfur and other elements. The term lipid is used to classify a large number of substances having very different physical - chemical characteristics, being its solubility in organic non-polar solvents the common property for their classification.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
